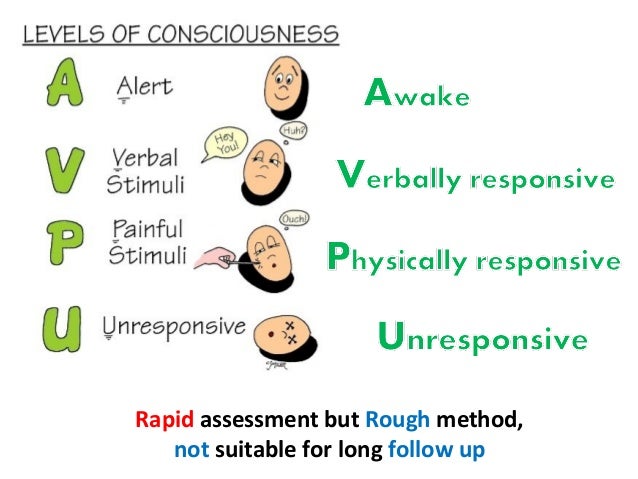
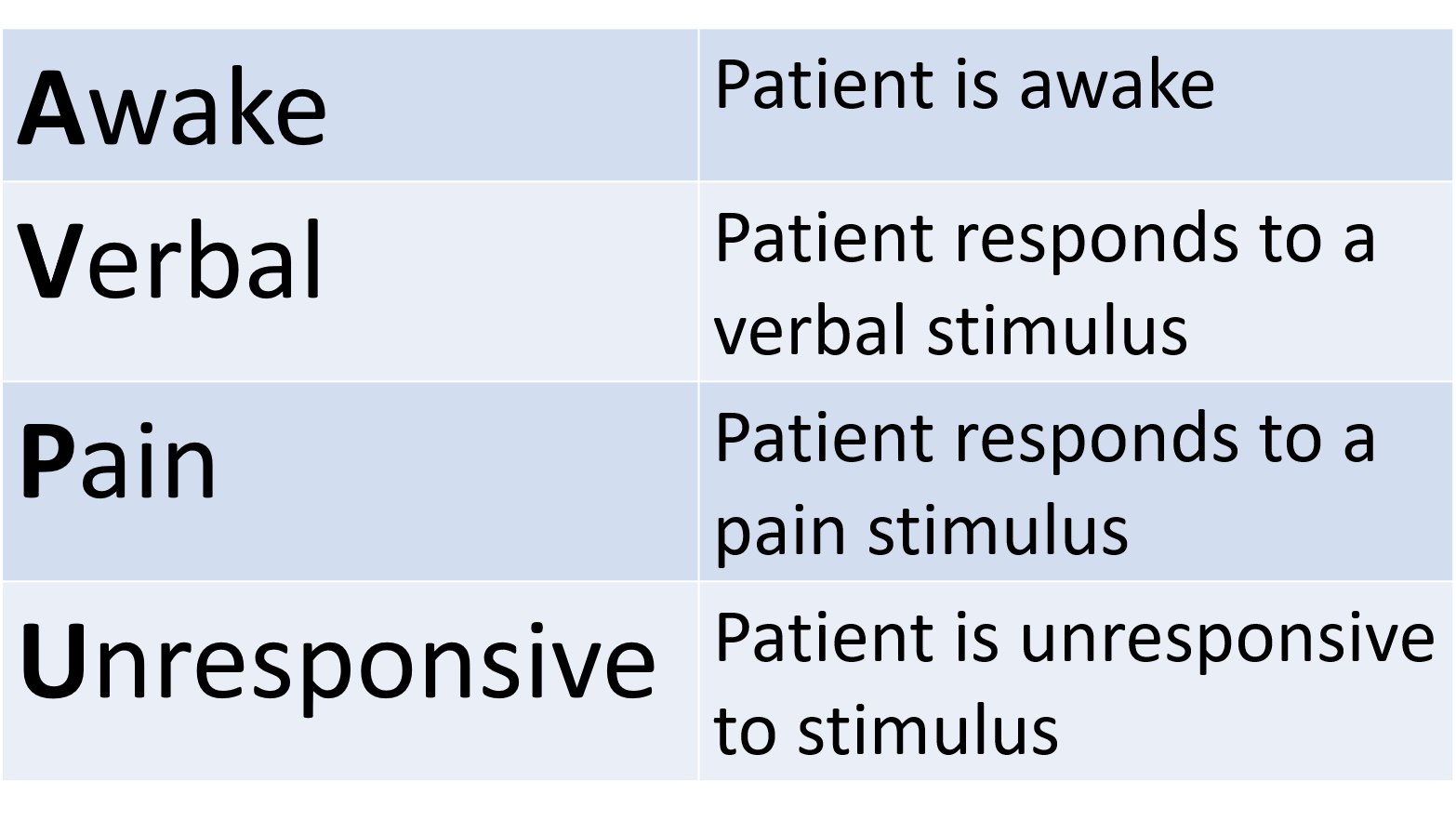
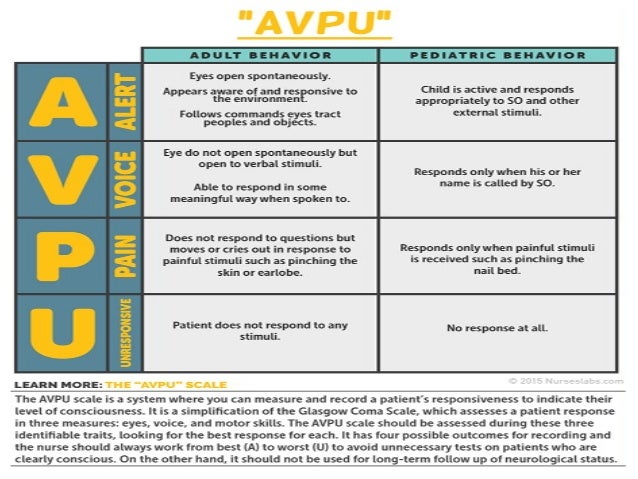
Nov 02, 16 · Perform a rapid neurological assessment using the AVPU mnemonic A – Alert V – Responding to Verbal stimuli P – Responding to Painful stimuli U – Unresponsive Examine pupils are responding appropriately to light An altered level of consciousness indicates the need for repeated evaluation of the patient's oxygenation, ventilationJun 28, 08 · Each of the five examples includes an assessment of the central nervous system or level of consciousness, although the methods used are not identical 37 These scores have yet to be scientifically validated;Nov , 19 · 10 7LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS • Consciousness is the patient's wakefulness and ability to respond to the environment • Level of consciousness is the most sensitive indicator of neurologic function • To assess level of consciousness, the examiner observes for alertness and ability to follow commands

Assessment Of Level Of Consciousness Following Severe Neurological Insult In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 60 Issue 5 1984
How do you assess neurological status
How do you assess neurological status-Assessment of Level of Consciousness A Stimulate with progressively stronger stimuli i) normal voice ii) shout iii) light touch iv) pain Observe patient's response (verbal or motor) If there is no response to voice or light touch, painful stimulus is needed to assess neurological status Central pain should be used firstMay 04, 21 · FPnotebookcom is a rapid access, pointofcare medical reference for primary care and emergency clinicians Started in 1995, this collection now contains 6936 interlinked topic pages divided into a tree of 31 specialty books and 736 chapters



Focused Neurological Assessment In 21 Nursing School Notes Medical School Studying Nursing School Survival
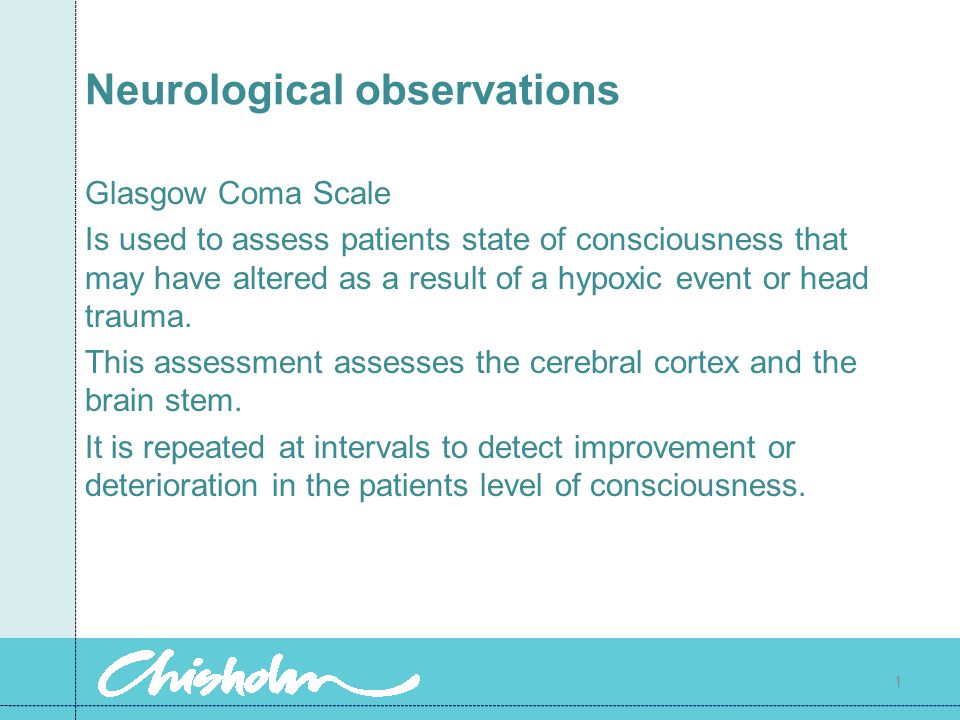
However, we have shown the importance of neurological assessment in identifying patients who might require escalation to a criticalA It provides data about level of consciousness only b It is considered equivalent to a complete neurologicMar 22, 15 · Level of Consciousness Assessment of the level of consciousness is the most important aspect of the neurological examination In most situations, a patient's level of consciousness deteriorates before any other neurological changes are noticed These deteriorations often are subtle and must be monitored carefully
May 09, 17 · Definitions Neurological observations are those investigations and examination that relate to the assessment of the nervous system These commonly focus upon six key areas Level of consciousness Pupillary activity Motor function Sensory function FAST (stroke recognition) Vital signs One observation that is commonly part of a neurological assessment (although primarilySep 05, 19 · This assessment is done immediately following the head trauma In some cases, it can be done on an ongoing basis to monitor the progress or regress of the condition relative to a baseline test We recommend that patients undergo consistent testing for 3 days in a row after they've suffered a head trauma Neurological AssessmentsApr 27, 18 · In this lesson we're going to talk about the different levels of consciousness This, plus your pupillary assessment are going to be the staples of your neuro exam We'll talk more about the pupillary assessment in the routine neuro assessments lesson In order to understand the varying levels of consciousness, we need to know what normal is
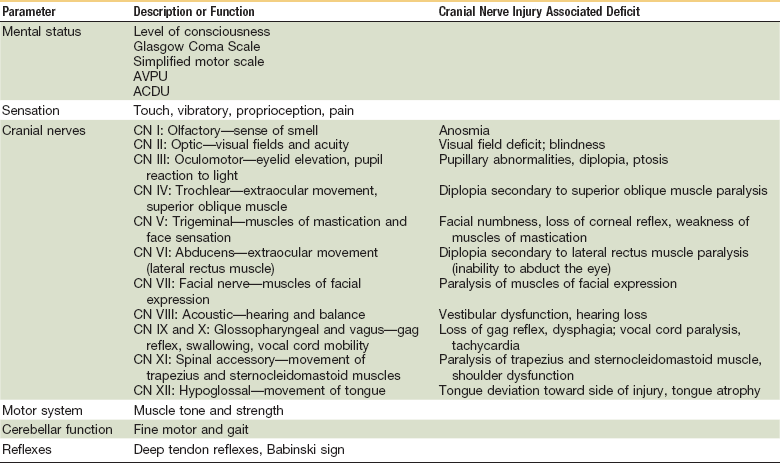
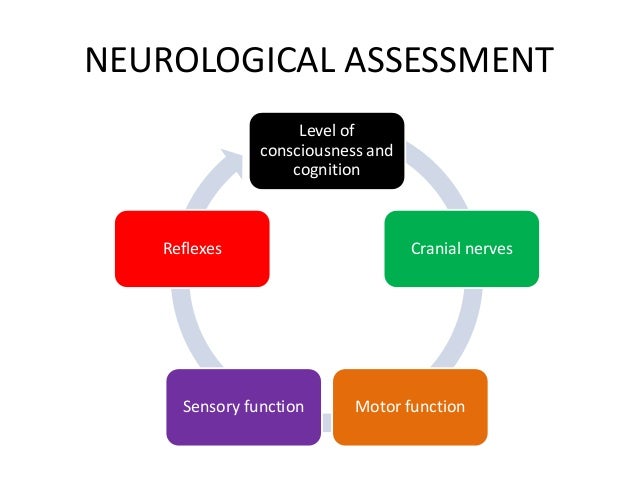
Neurological assessment, describes assessment of level of consciousness ONSCIOUSNESS Consciousness is defined as the state of being aware of physical events or mental concepts Conscious patients are awake and responsive to their surroundings (Marcovitch, 05) The level of consciousness has been described as the degree of arousal and awarenessNursing Neuro Assessment The initial assessment should be a comprehensive exam covering several critical areas • Level of consciousness and mentation • Movement • Sensation • Cerebellar function • Reflexes • Cranial nerves This initial exam will establish baseline data with which to compare subsequent assessment findingsRegistered users can save articles, searches, and manage email alerts All registration fields are required



1 Neurological Assessment At The End Of This Self Study The Participant Will 1 Describe The Neuro Nursing Assessment 2 List 5 Abnormal Findings In A Neuro Ppt Download



Neurological Assessment In Children Nurse Key
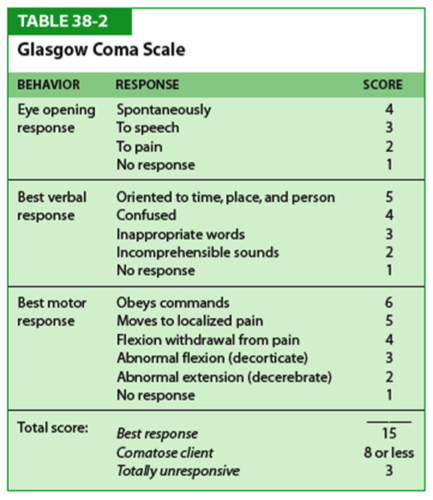
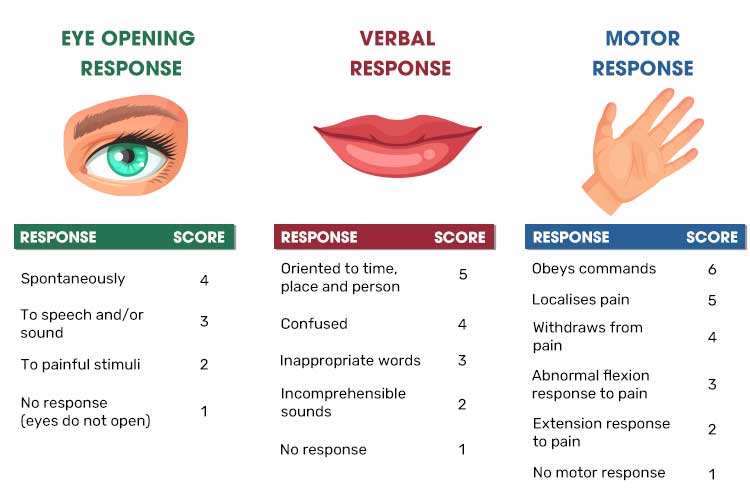
Neurological Assessment Possible locations for leg weakness Primary motor cortex Corticospinal track (from primary motor neuron down to lower motor neuron in lumbar cord) Lower motor neuron Efferent projection of motor neuron Neuromuscular junction Muscle Metabolic Neurological Assessment History of present complaint Level of consciousness andNeurological Observation Chart The EP mirrors the flow of the Adult Neurological Observation Chart ALERT / REMINDER IT IS NOT ONLY FOR USE ON NEURO A NEUROLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IS CONDUCTED TO DETERMINE LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS IRRESPECTIVE OF THE CAUSE OR THE SETTING SURGICAL OR NEUROLOGY PATIENTSATIENTSNEUROLOGICAL ASSESSMENT Neurologic assessment includes • Cognitive function • Reflexes • History • Level of consciousness • Glasgow Coma Scale o Pupillary response o Speech o Behaviour o Motor function Cognitive Function • Memory • Knowledge • Judgment Eg 1 Instrument MMSE(mini mental state examination) • Orientation • Registration • Attention &



Advanced Neuro Assessment Ppt Download



Neurological Assessment97 03
•A change in LOC is the earliest & MOST sensitive indication of a change in the patients' neuro status!Neurological assessment Part 1assessing level of consciousness Neurological assessment Part 1assessing level of consciousness Nurs Times 08 Jul 814;104(27)267 Author Phil Jevon 1 Affiliation 1 Manor Hospital, Walsall PMID No abstract availableJul 14, 16 · Level of Consciousness Assessment The LOC is assessed by applying stimuli and observing the response The technique used depends on the type of stimuli applied Auditory and tactile stimuli are the two used to assess consciousness and are considered on a



Neuro Assessment


8 Neurologic Evaluation And Management Pocket Dentistry
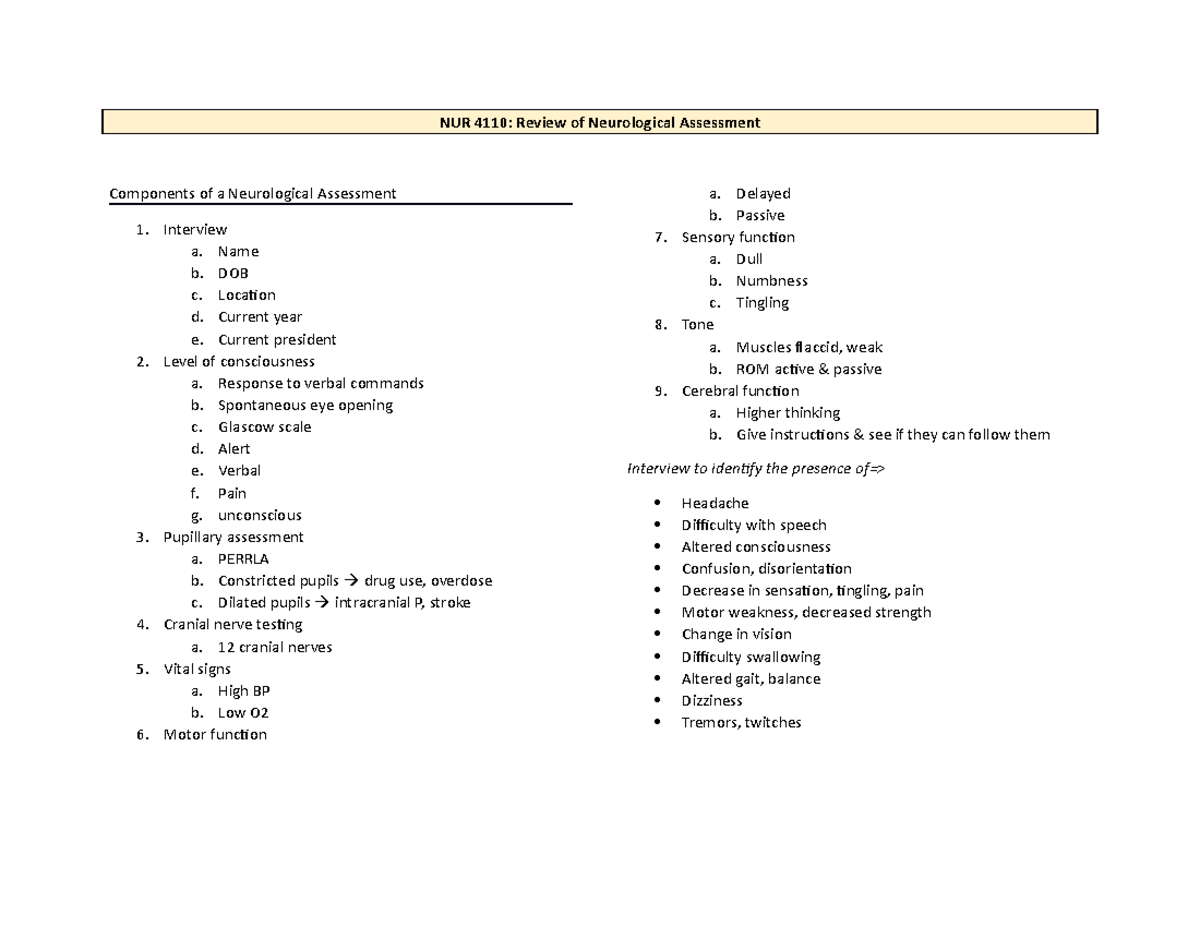
Neurological Altered Level of Consciousness (LOC) Level of responsiveness and consciousness is the most important indicator of the patient's condition LOC is a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition (consciousness) to coma Altered LOC is not the disorder but the result of a pathology Coma Unconsciousness, unarousable unresponsivenessMar 27, 18 · Assess Level of Consciousness An individual's level of consciousness can deteriorate due to many different reasons, such as head injuries, increased intracranial pressure, haemorrhage, or lesions and tumours Determining the level of consciousness depends on the individual you are assessing and can be easy or difficultMay 01, 1984 · An alternative method of coma assessment is presented and compared with the Glasgow Coma Scale The merits of the Comprehensive Level of Consciousness Scale as a research tool are presented An analysis of 101 consecutive consciousnessimpaired patients with their shortterm outcome is presented



Levels Of Consciousness Neuro Assessment Youtube


Assessment Of Consciousness
Jun 21, 05 · Assessing a patient's level of consciousness is an essential component of a neurological examination, which is usually performed alongside an assessment of pupil size and reaction, vital signs and focal neurological signs in the limbsFor rapid neurologic assessment of traumatic patients and advanced life support It has also been used by paramedics of hospital as well as medical settings for critically ill patients and poisoned patients (1,5) It is a simple method of assessing level of consciousness according to response to verbal or painful stimuli (1)**because below level of consciousness, comatose patients with no bleeds or injuries should still have reflexes because pain is the last sensation to go 4 types deep tendon reflexes, superficial, visceral, pathologic (abnormal)



Evaluating The Neurologic Status Of Unconscious Patients American Nurse



Assessment Of Level Of Consciousness Following Severe Neurological Insult In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 60 Issue 5 1984
Nov 24, · If you're learning how to do neuro checks, one of the most challenging aspects can be distinguishing level of consciousness Often, this is the first thing to change when neurologic damage is occurring But it's very subtle and can be difficult to detect¾Review Neurological Assessment ¾Discuss the basic neuroanatomy and physiology ¾Describe the pathophysiology, management and nursing interventions of ¾Hydrocephalus ¾Cerebrovasculardisease ¾Meningitis ¾Seizures/status epilepticus ¾Head/Spinal Cord Injury ¾Neuromuscular Disorders Basic Neurologic Exam •Level of consciousnessA deficit in the level of consciousness suggests that both of the cerebral hemispheres or the reticular activating system have been injured A decreased level of consciousness correlates to increased morbidity (sickness) and mortality (death) Thus it is a valuable measure of a patient's medical and neurological status



Neurological Assessment Ed Areyouprepared



Emergency Care Interventions Neurological Assessment Ppt Video Online Download
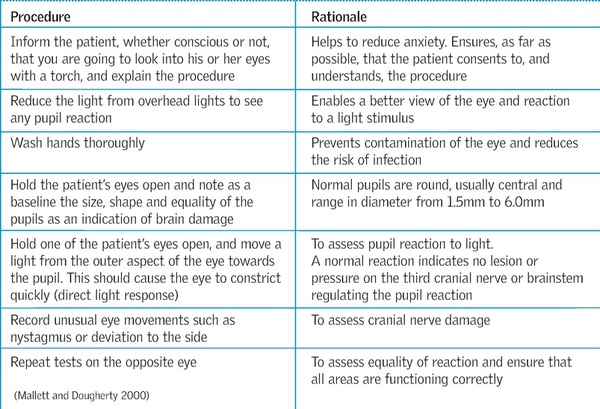
Medical Control Guideline LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS PRINCIPLE 1 Evaluation and documentation of the patient's level of consciousness are key components of a thorough patient assessment 2 The patient's baseline level of consciousness should be taken into consideration when evaluating whether the altered level of consciousness (ALOC) findingNeurological assessment wwwwestafricaneducatednursesorg Feb 6, 16 pg 8 Levels of Consciousness Table 2 Levels of Consciousness Full consciousness The patient is alert, attentive, follows commands, responds promptly to external stimulation if asleep, and once awake, remains attentiveApr 01, 04 · B) measures level of consciousness C) less valid when used by inexperienced users D) is the only scale in the world where you can be dead and still score 3 Pupil size is recorded as well as the pupils reaction to light The size that is recorded should be the size of the pupilA) in the ambient light of the room



Levels Of Consciousness Neuro Assessment Youtube



Obtunded Somnolent Brain Dead Neuro Assessment Neurological Assessment Nursing Assessment Icu Nursing
Unexplained decrease in level of consciousness or failure to awaken, especially after TBI or stroke) 3 Test Cranial Nerves (see next pages for CN and brainstem testing) In rapid neurologic examination, pupil assessment is the primary CN examination Loss of reactivity toLevel of consciousness Always begin the exam by introducing yourself to the patient as a tool to evaluate the patient's gross level of consciousness Is the patient awake, alert and responsive?Like any other aspect of the exam, the neurological assessment has limits Testing of one system is often predicated on the normal function of other organ systems If, for example, a patient is visually impaired, they may not be able to perform finger to nose testing, a part of the assessment of cerebellar function (see below)



1 Neurological Assessment At The End Of This Self Study The Participant Will 1 Describe The Neuro Nursing Assessment 2 List 5 Abnormal Findings In A Neuro Ppt Download



Pdf Assessing Level Of Consciousness And Cognitive Changes From Vegetative State To Full Recovery
However, we have shown the importance of neurological assessment in identifying patients who might require escalation to a critical care area and in theTwo really important parts of neurological assessment are level of consciousness and mental status In fact, level of consciousness is THE most basicMay 19, · Neurological deterioration can be defined as a decrease of two or more points on the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Patients may present in a variety of consciousness states ranging from full alertness and awareness, to some level of impairment, to complete unawareness and unresponsiveness


Coma Scales A Historical Review


Level Of Consciousness Cranial Nerves Medschool
Assessing level of consciousness and cognitive changes from vegetative state to full recovery proper cognitive assessment are critical for the rehabilitation of patients functioning to high cognitive ability levels, combining a breadth of neuropsychological assessments with structural and functional imaging•Sedation should be stopped or decreased for an accurate assessment Level of Consciousness 7 NeuroTrauma LA 13 OUTCOME OPTIMIZATION LACUSC •The technique of evaluation of the patient with an altered level of consciousness can be divided into three phases The first is to determine the level of consciousness itself Second is evaluation of the patient, searching carefully for hints as to the cause of the confusion or coma



Neuro Assessment


Assessment Of Neurological Functioning Avpu Deteriorating Patient Assessment Recognition And Management
Feb 08, 18 · Neurological assessment For Nurses 1 NEUROLOGICAL INJURY ASSESSMENT & MANAGEMENT Shibu Chacko 2 Learning Outcomes Know when and why a neurological assessment must be performed To be able to carry out a neurological assessment on a patient with an actual/potential altered level of consciousness using the AVPU score and Glasgow Coma Scale Know common causes of altered conscious levelMay 13, · Medical illness, traumatic brain injury, alcohol intoxication, drugs, and poisonings may all lead to aberrations in a patient's neurological and physiological status in ways that cause an abnormal level of consciousness AVPU is a straightforward scale that is useful to rapidly grade a patient's gross level of consciousness, responsiveness, or mental status It comes into playIncludes an assessment of the central nervous system or level of consciousness, although the methods used are not identical 3–7 These scores have yet to be scientifically validated;



Neuro Assessment In 5 Easy Steps West Region Ems Trauma


The Glasgow Coma Scale And Other Neurological Observations
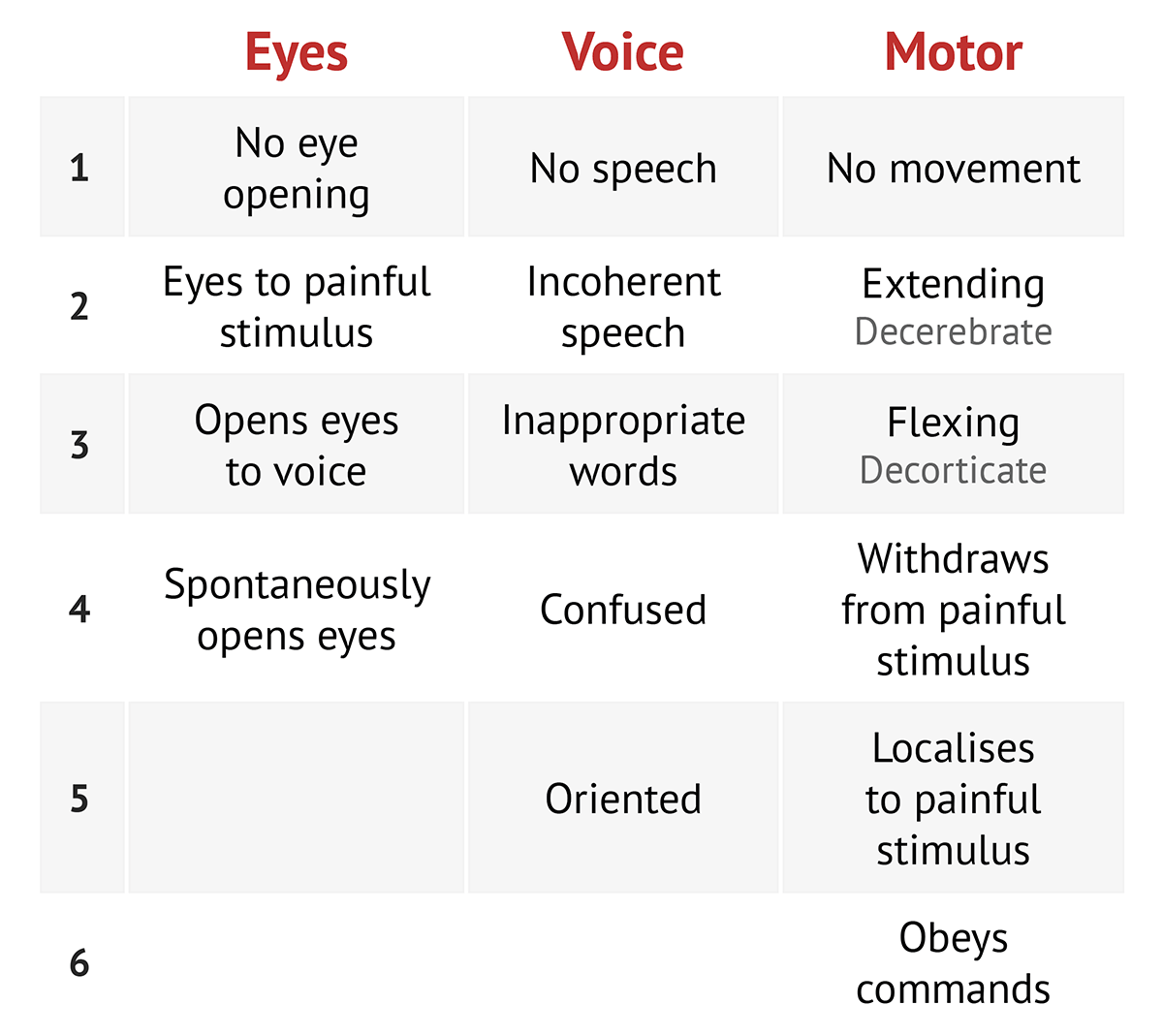
ACUTE ASSESSMENT SCALES GLASGOW COMA SCALE (GCS) • Identifies ocular, verbal, and motor response to examination • Tool is used to communicate the level of consciousness (LOC) of patients with an acute brain injury • The scale was developed to complement and not replace assessments of other neurological functions • Strength Fast andAug 30, 17 · A neurological assessment involves thoroughly assessing a patient's level of consciousness, motor function and pupillary reaction The purpose of a neurological assessment is to detect abnormalities that may suggest brain injury, or diseaseAims and objectives To study practice in consciousness assessment among neuroscience nurses in Europe Background Over the years, several instruments have been developed to assess the level of consciousness for patients with brain injury It is unclear which instrument is being used by nurses in Europe and how they are trained to use these



Strengthening Your Neurologic Assessment Techniques Article Nursingcenter



Neurological Assessment
A patient is admitted to the critical care unit with a subdural hematoma The GCS is used to assess his level of consciousness Which statement is true concerning the GCS?If not, then the exam may have to be abbreviated or urgent actions may have to be taken



Amp Pinterest In Action Nursing Assessment Neurological Assessment Nursing Physical Assessment



Neurological Assessment August 17 V 2 1 1



European Academy Of Neurology Guideline On The Diagnosis Of Coma And Other Disorders Of Consciousness Kondziella European Journal Of Neurology Wiley Online Library



Focused Neurological Assessment In 21 Nursing School Notes Medical School Studying Nursing School Survival



Neurological Assessment



Neurological Exam Level Of Consciousness Freshrn



Assessment Nurse Key



Levels Of Consciousness Neuro Assessment Youtube
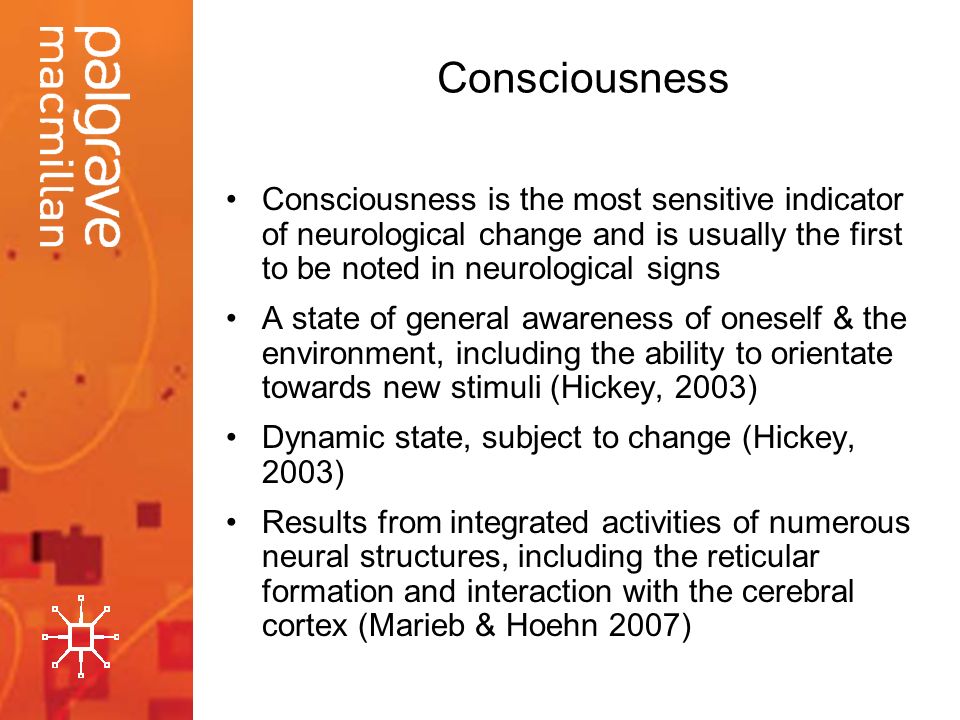


Emergency Care Interventions Neurological Assessment Ppt Video Online Download



Invited Commentary Stroke Assessment In The Covid 19 Era The Observational Neurologic Exam Neurology Blogs
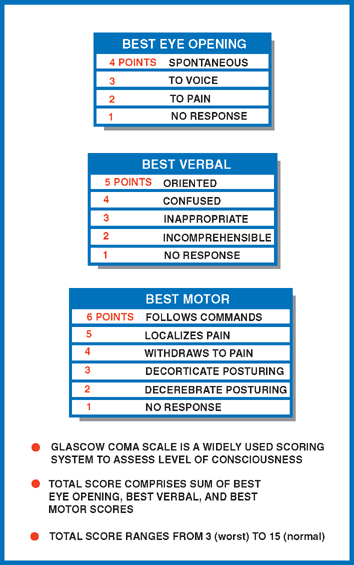


Consciousness Neupsy Key



1 Neurological Assessment At The End Of This Self Study The Participant Will 1 Describe The Neuro Nursing Assessment 2 List 5 Abnormal Findings In A Neuro Ppt Download



Neurological Assessment Musculoskeletal Key



Pdf The Glasgow Coma Scale In Adults Doing It Right
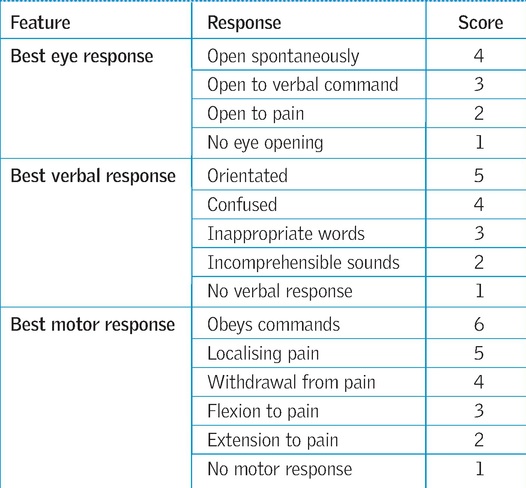


The Glasgow Coma Scale And Other Neurological Observations



1 Levels Of Consciousness Assessment Of Levels Of Consciousnessincludes Following Categories Levels Of Consciousness Neurological Assessment Medical Knowledge



Abbreviated Assessment Ppt Video Online Download
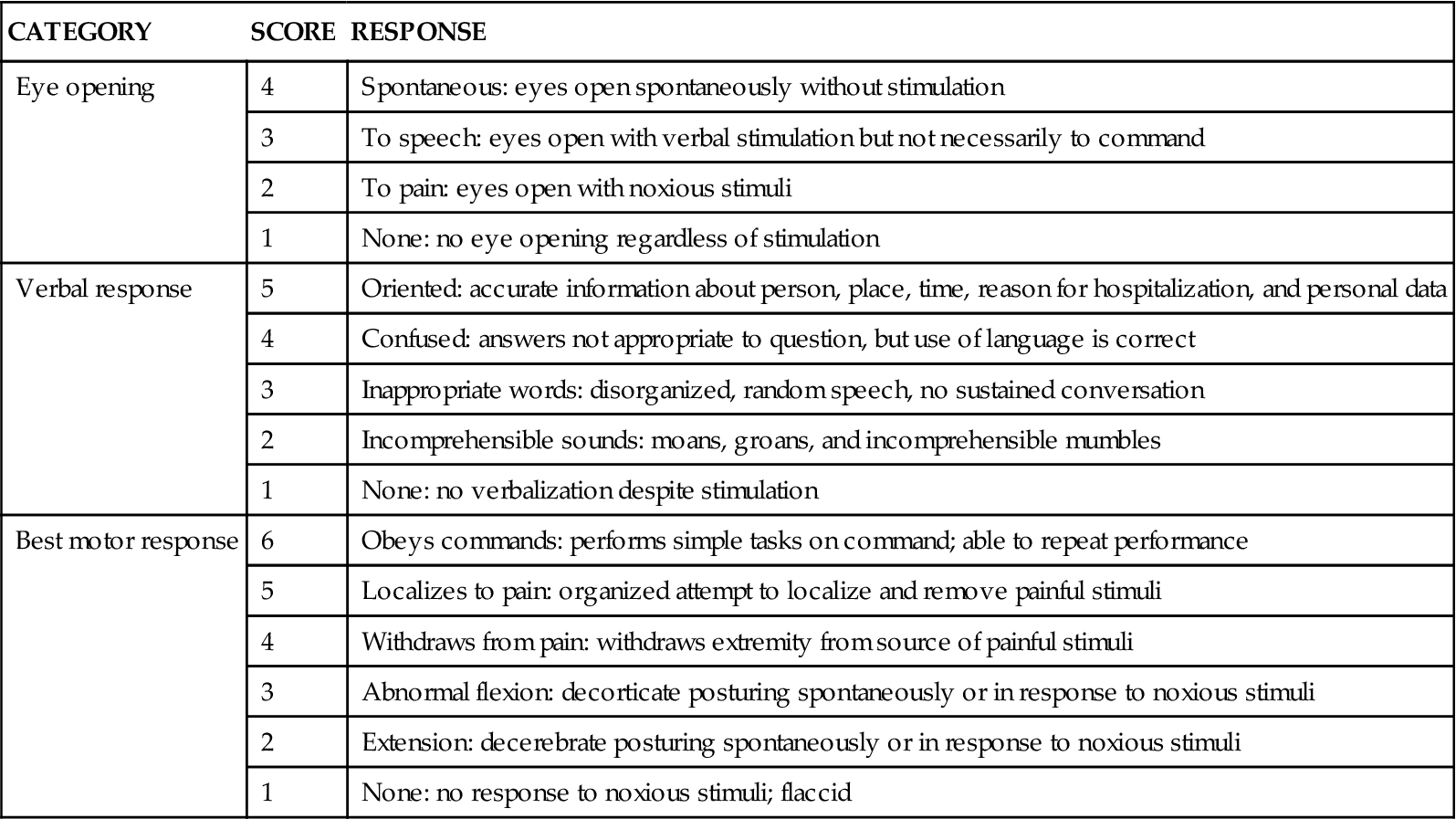


Neurological Clinical Assessment And Diagnostic Procedures Clinical Gate



Neurological Assessment Flashcards Quizlet


Neuro Cs Review Flashcards Quizlet


Causes Of Acute Neurological Deterioration Ausmed



Emergency Care Interventions Neurological Assessment Ppt Video Online Download


How To Use Avpu To Check Level Of Consciousness



Bvns Neurotransmitter 2 0 Technically Speaking September 16 Bush Veterinary Neurology Service


Neurological Assessment



Guidelines For A Brief Neurological Nursing Assessment In Acute Care A Literature Review Semantic Scholar



Ingenius Level Of Consciousness Assessment Avpu The Facebook



Neuro Assessment Coma Anatomical Terms Of Motion



Neurological Assessment For Nurses



New Improved Physical Assessment Neurological Overview This Course


Assessment Of Neurological Functioning Avpu Deteriorating Patient Assessment Recognition And Management



Chapter 06 Neuro Brainstem Coma



Assessment Of Level Of Consciousness Following Severe Neurological Insult In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 60 Issue 5 1984



Investigating Factors That Have An Impact On Nurses Performance Of Patients Conscious Level Assessment A Systematic Review Semantic Scholar



Words Used To Describe Level Of Consciousness Download Table



Neurological Assessment Human Anatomy Nervous System



What Does Acvpu Stand For First Aid For Free



Guidelines For Basic Adult Neurological Observation Ccso 14



Neurological Assessment Cheat Sheet With Glascow Coma Scale Download Your Free Copy Today Nursecepts N Neurological Assessment Nursing Notes Nervous System



Neurological Assessment 1 Assessing Level Of Consciousness Nursing Times



Words Used To Describe Level Of Consciousness Download Table



Neuro Assessment Hdsp Final 10 09



Emergency Care Chapter Interventions Neurological Assessment Emergency



Neurological Assessment Visual Acuity Foot



1 Neurological Assessment At The End Of This Self Study The Participant Will 1 Describe The Neuro Nursing Assessment 2 List 5 Abnormal Findings In A Neuro Ppt Download



Coma A Systematic Approach To Patient Evaluation And Management 03 05 19 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing



Nvs Coma Animal Anatomy



Flow Chart Level Of Consciousness Assessed At Mri And Icu Discharge Download Scientific Diagram



Neurological Assessment Level Of Consciousness


Neurological Assessment 3 Studocu


Neurological Observations Ppt Video Online Download


Assessment Of Consciousness



Avramov S Scale To Assess The Level Of Consciousness 16 Download Table



Chapter Neurological Assessment Neurological Assessment Rachel Palmer


Assessment Of Consciousness



Amazon In Buy Neurologic Assessment Diminished Level Of Consciousness Book Online At Low Prices In India Neurologic Assessment Diminished Level Of Consciousness Reviews Ratings



Glasgow Coma Scale Gcs Neurological Scale Tool Assess The Level Of Consciousness In A Patient Youtube



Neurological Assessment At The Time Of Inclusion Download Table
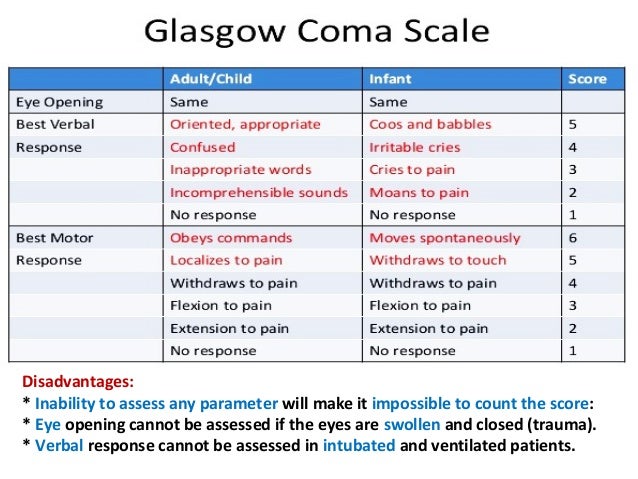


Assessment Of Consciousness



Levels Of Consciousness Assessment For Nurses Loc Youtube



Neurological Assessment Nurse Key



Neurological Assessment Anatomical Terms Of Motion Coma



Neurological Assessment And Gcs



Neuro Assessment Coma Nervous System



The Neurology Of Consciousness 2nd Edition


Assessing The Level Of Consciousness Hku E Learning Platform In Clinical Neurosciences



Decorticate And Decerebrate Posturing What Does It Really Tell Us Ryansilverthorn Com Medical School Prep Neurological Assessment Lower Extremity



Neurological Assessment Nurse Key



Neurological Assessment Sp07 Webversion
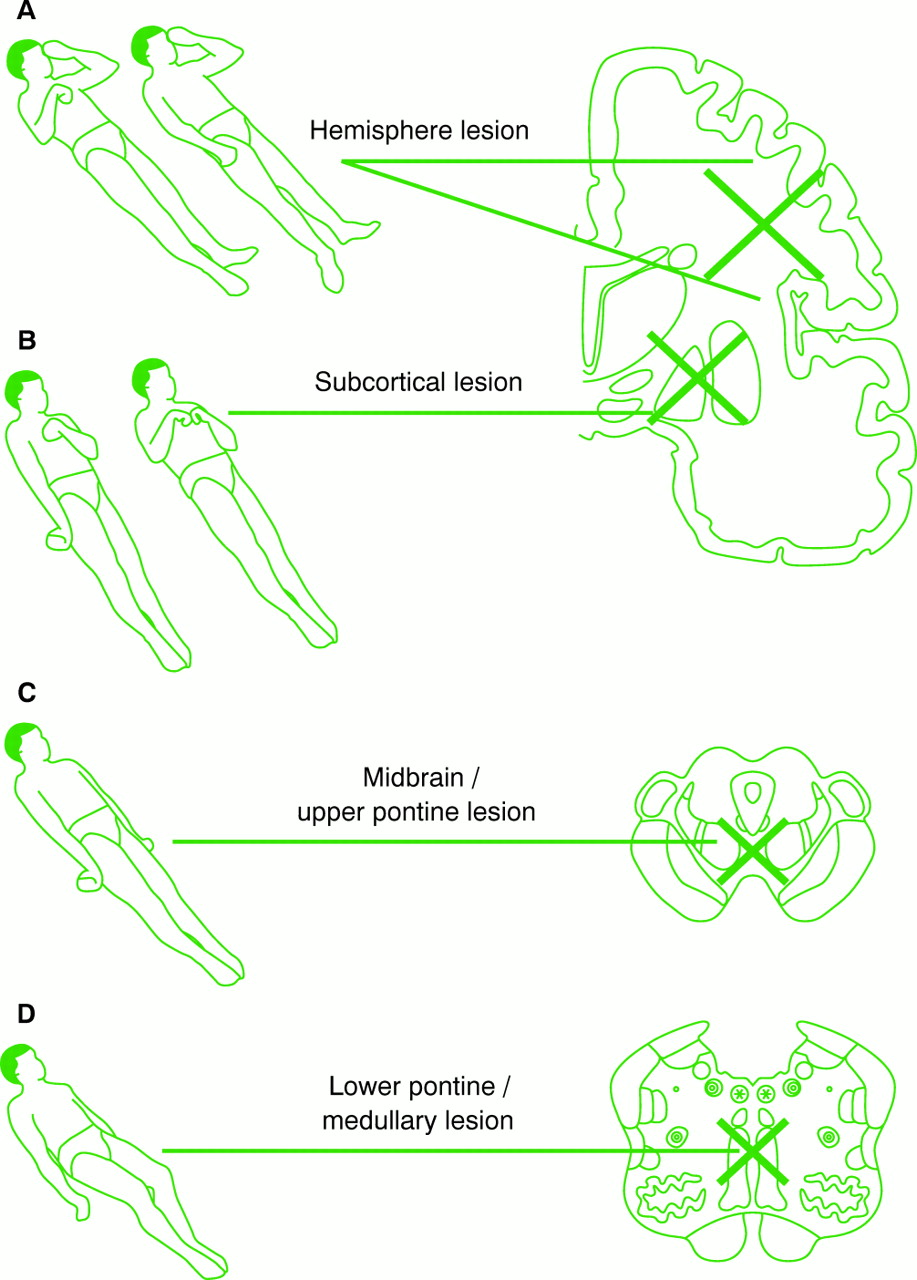


Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry



Neurological Assessment And Gcs



Chapter Neurological Assessment Neurological Assessment Rachel Palmer



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿